Default Static Route
1. Introduction
🔍 What is a Default Static Route?
A default static route is a manually configured route that forwards traffic destined for unknown networks to a specific next-hop address or exit interface. It ensures packet delivery even when the routing table lacks a specific route for the destination.
🛠️ Why is it Important for Network Functionality?
In real-world networks, configuring routes for every possible destination is impractical. A default static route simplifies the routing process by providing a fallback option.
Example: A local network can communicate with the internet through an ISP router when no specific routes are defined.
2. Key Concepts
🔍 Default Route Basics
When a router encounters traffic destined for an unknown network, it consults its routing table to determine how to handle the traffic.
Without a Default Route
- The router drops packets if no matching route exists in the table, interrupting communication with external networks.
With a Default Route
- The router forwards traffic to a pre-configured gateway, called the Gateway of Last Resort, which directs packets toward their final destination.

🛠️ Practical Example

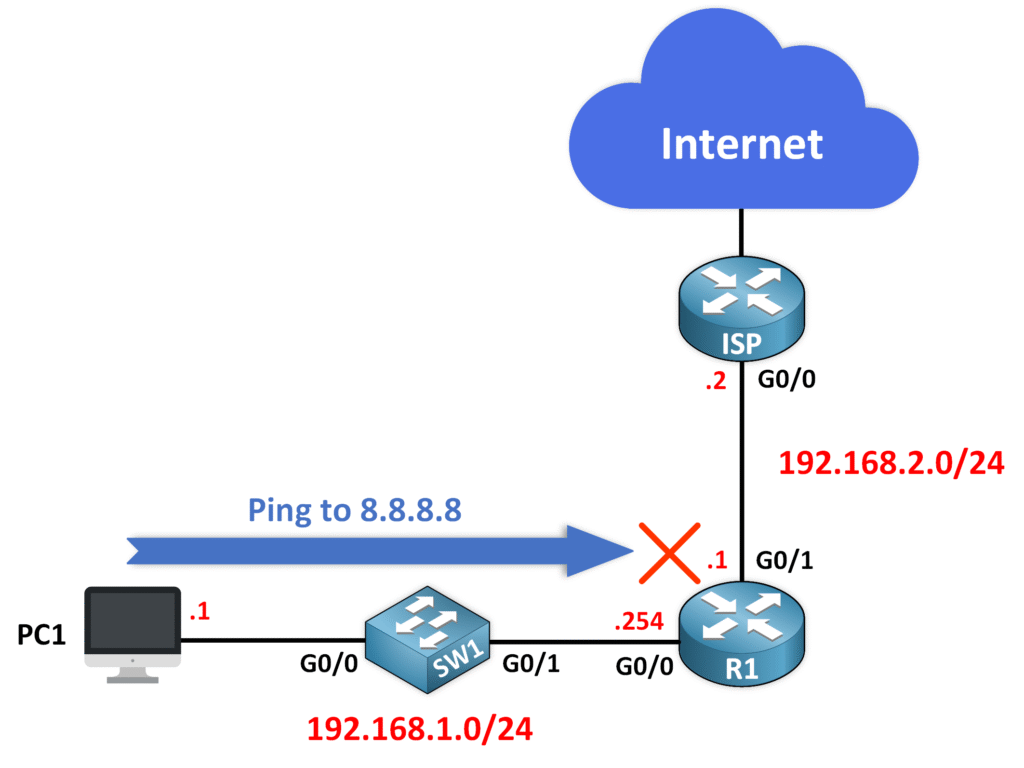
Consider a network where router R1 is connected to:
- PC1 (192.168.1.0/24)
- ISP router at 192.168.2.2
✅ Scenario: If PC1 pings 8.8.8.8, the router’s behavior depends on whether a default route is set:
🔹 Without a Default Route
- R1 drops the packets since no route to
8.8.8.8exists.

🔹 With a Default Route
- R1 forwards the packets to
192.168.2.2(the ISP), enabling communication with the internet.

3. Configure Default Static Route
🔹 Default Static Route Command
To configure a default static route on R1, use the following command:
R1# configure terminal R1(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.2
0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0: Matches all possible destinations.192.168.2.2: Specifies the next-hop address (the ISP router).
🛠️ Step-by-Step Example
🚫 Before Configuration
R1’s routing table only includes directly connected networks:
R1# show ip route
Gateway of last resort is not set
192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 192.168.1.254/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
192.168.2.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L 192.168.2.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
If PC1 pings 8.8.8.8, R1 drops the traffic because it has no instructions for forwarding unknown destinations.
✅ After Configuration
Adding a default static route updates the routing table, setting the Gateway of Last Resort:
R1# show ip route
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.2.2 to network 0.0.0.0
192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 192.168.1.254/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
192.168.2.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.2.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
L 192.168.2.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 192.168.2.2
4. Verification and Troubleshooting
🔍 Verifying the Configuration
To confirm the default route is working, test connectivity by pinging 8.8.8.8 from PC1. The traffic should be forwarded by R1 to the ISP.
🔹 Command on PC1:
PC1> ping 8.8.8.8 Pinging 8.8.8.8 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 8.8.8.8: bytes=32 time=10ms TTL=56 Reply from 8.8.8.8: bytes=32 time=11ms TTL=56 Reply from 8.8.8.8: bytes=32 time=10ms TTL=56 Reply from 8.8.8.8: bytes=32 time=11ms TTL=56

Results Analysis:
- Successful Response: Confirms R1 used the default route to forward traffic to the ISP.
- Failure (No Reply): Check the following:
- Is the next-hop address (
192.168.2.2) correct? - Are interfaces active and properly connected?
- Is there any ACL or security policy blocking the traffic?
- Is the next-hop address (
5. 📢 Conclusion
A default static route ensures that a router can forward packets to unknown destinations, acting as a gateway of last resort. It is a crucial configuration for enabling internet access !
